Understanding Your Menstrual Cycle: A Comprehensive Guide to Its Phases and Symptoms
The menstrual cycle is a natural, recurring process that occurs in most women of reproductive age. It involves a series of hormonal changes that prepare the body for a potential pregnancy each month. Understanding the menstrual cycle is not only essential for women’s health but also helps in identifying any irregularities that may require medical attention. In this article, we’ll explore the various phases of the menstrual cycle, the symptoms that accompany each stage, and how to track your cycle effectively.
What is the Menstrual Cycle?
The menstrual cycle is a monthly series of changes that a woman’s body goes through to prepare for pregnancy. It typically lasts between 21 and 35 days, with the average cycle being around 28 days. The cycle is regulated by a complex interaction of hormones, including estrogen, progesterone, and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). These hormones cause changes in the ovaries and the lining of the uterus, preparing the body for a possible pregnancy.
If pregnancy does not occur, the uterine lining is shed, leading to menstruation. This is the first day of the menstrual cycle and marks the beginning of the process once again.
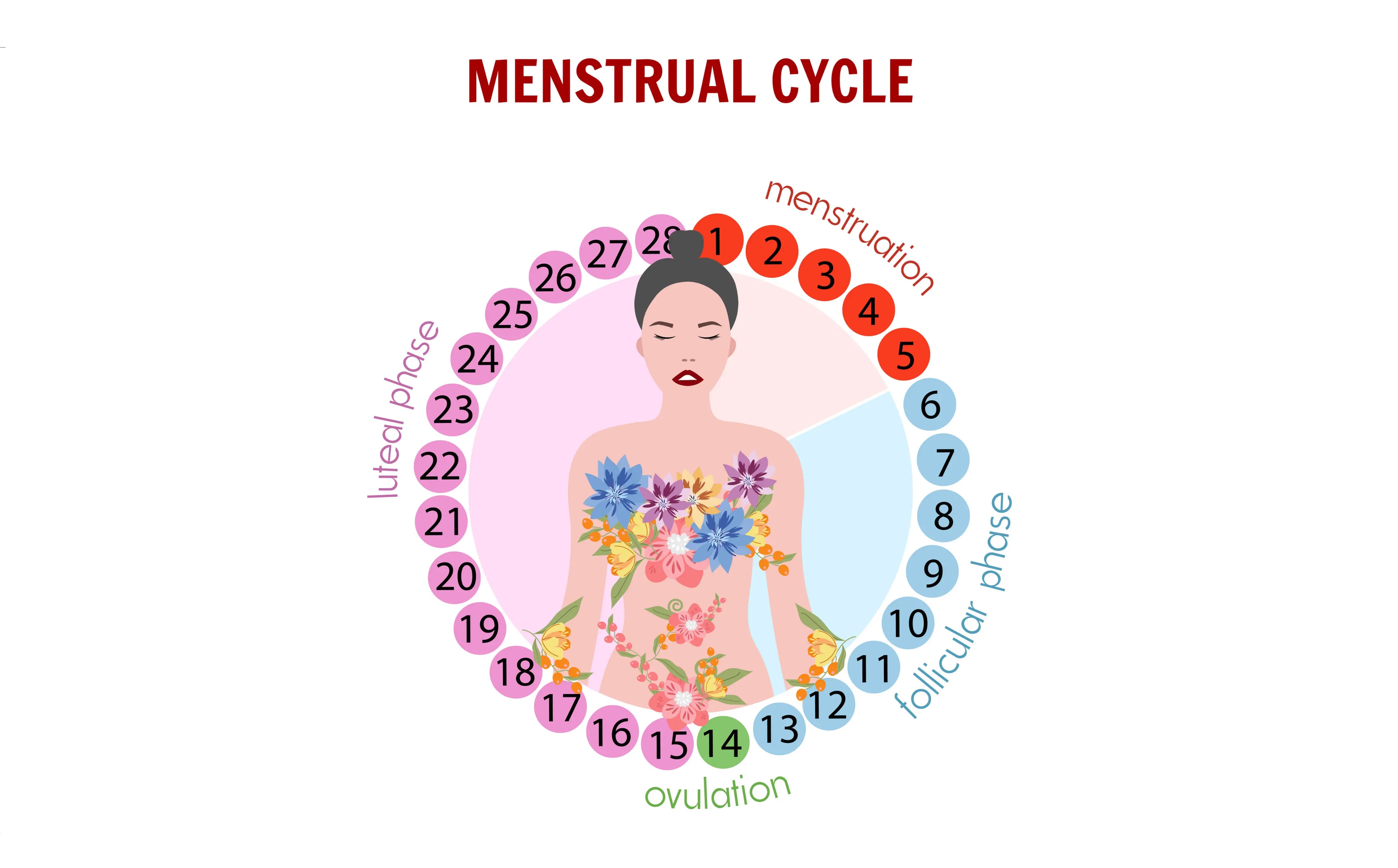
The Four Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
The menstrual cycle is generally divided into four phases, each with its own distinct hormonal and physical changes. These phases are:
1. Menstrual Phase (Day 1-5)
What Happens: This phase starts with the first day of menstruation, where the uterine lining is shed through vaginal bleeding. It usually lasts anywhere from 3 to 7 days. Hormone levels (estrogen and progesterone) are at their lowest during this phase, which is why many women experience symptoms like cramps, headaches, and fatigue.
Symptoms:
Bleeding (varying in flow)
Cramps
Lower energy levels
Irritability
Headaches or back pain
Tracking Tips: During the menstrual phase, it’s a good time to track the start and end of your period, as well as your flow level (light, medium, or heavy).
2. Follicular Phase (Day 1-13)
What Happens: The follicular phase overlaps with the menstrual phase, starting on the first day of menstruation and lasting until ovulation. During this phase, the body starts to prepare for ovulation. The pituitary gland releases FSH, stimulating the growth of follicles in the ovaries. Each follicle contains an egg, and one will mature into an egg ready for release.
Symptoms:
Increasing energy
Clearer skin
Heightened libido
Less bloating or discomfort
Tracking Tips: Monitor any changes in your energy levels, skin, or mood. Many women feel more energetic and productive during this phase.
3. Ovulation Phase (Day 14)
What Happens: Ovulation typically occurs around day 14 in a 28-day cycle but can vary from woman to woman. A surge in luteinizing hormone (LH) causes the mature follicle to release an egg from the ovary. The egg travels down the fallopian tube, where it can be fertilized by sperm if sexual intercourse occurs. This is the most fertile period of the cycle.
Symptoms:
Increased cervical mucus (clear and slippery)
Mild pelvic pain (mittelschmerz)
Increased sexual desire
Heightened sense of smell or taste
Tracking Tips: Use ovulation predictor kits or track changes in your cervical mucus to identify your most fertile days. Many women experience slight pelvic discomfort or cramping when ovulating.
4. Luteal Phase (Day 15-28)
What Happens: After ovulation, the luteal phase begins. The ruptured follicle turns into a structure called the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone. This hormone helps thicken the uterine lining in preparation for a fertilized egg. If the egg is not fertilized, the corpus luteum breaks down, leading to a drop in progesterone, and the cycle starts again with menstruation.
Symptoms:
Bloating
Mood swings or irritability
Breast tenderness
Fatigue
Food cravings (especially sweet or salty)
Tracking Tips: This phase is often when PMS (premenstrual syndrome) symptoms occur. Tracking your mood, energy levels, and any physical changes like bloating or sore breasts can help you prepare for the start of your period.
Common Symptoms Throughout the Menstrual Cycle
While each phase comes with its own set of symptoms, many women experience common issues throughout their cycle. These include:
Cramps (Dysmenorrhea): Painful cramping is most common during the menstrual and follicular phases. It occurs when the uterus contracts to expel the lining. Over-the-counter pain relievers or heat therapy can help alleviate this discomfort.
Headaches: Hormonal fluctuations can trigger headaches or migraines, especially around ovulation or during the luteal phase.
Mood Swings: Hormonal changes, particularly in the luteal phase, can lead to irritability, anxiety, or feelings of depression.
Fatigue: Many women report feeling more tired during menstruation or the luteal phase due to hormonal shifts.
How to Track Your Menstrual Cycle
Tracking your menstrual cycle can help you understand your body’s patterns and better manage any symptoms. You can track your cycle using several methods:
Calendar Method: Mark the start and end of your period on a calendar. Calculate the length of your cycle and look for trends.
Basal Body Temperature (BBT): Your body temperature rises slightly after ovulation. Charting BBT can help predict ovulation and confirm when you’re most fertile.
Cervical Mucus Observation: The consistency of cervical mucus changes throughout the cycle. It becomes clearer and slippery around ovulation, making it a natural sign of fertility.
Period Tracker Apps: Many apps are available to help you track your cycle, symptoms, and mood. These apps often include reminders for important days, such as ovulation and menstruation.
Irregular Cycles and What They Mean
It’s normal for your menstrual cycle to vary slightly from month to month. However, if you experience irregular cycles (e.g., missing periods or very heavy bleeding), it could be a sign of an underlying health issue, such as:
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Thyroid Disorders
Endometriosis
Fibroids
Stress or Lifestyle Changes
If you notice significant changes in your cycle or experience symptoms like extreme pain or heavy bleeding, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation.
Conclusion: Empowering Yourself with Knowledge
Understanding your menstrual cycle is an empowering way to take control of your reproductive health. By learning about the different phases, tracking your symptoms, and recognizing when things are out of balance, you can make informed decisions about your health and well-being. Whether you’re trying to conceive, managing PMS, or simply wanting to understand your body better, knowledge of your menstrual cycle can provide valuable insights into your overall health.
Date: 2024-12-23
Author: Nazmul Shishir
Tags: menstrual cycle, menstrual health, phases of the menstrual cycle, ovulation, period tracking, PMS, menstrual symptoms, reproductive health, healthy period, menstruation guide, cycle phases, period tracking tips